Host Management Workflow
1. Management Logic Overview
Host management follows the closed-loop flow of “add hosts → group / filter → status monitoring → O&M operations”. By centrally managing VMOS hardware (compute boxes), it provides a stable underlying foundation for upper-layer cloud machine services.
2. Core Operation Steps
Step 1: Add and Onboard Hosts
Before use, you need to connect VMOS compute boxes to the management platform:
- Automatic discovery: When the PC client and VMOS L1 hosts are on the same subnet, the system automatically scans and discovers online hosts.
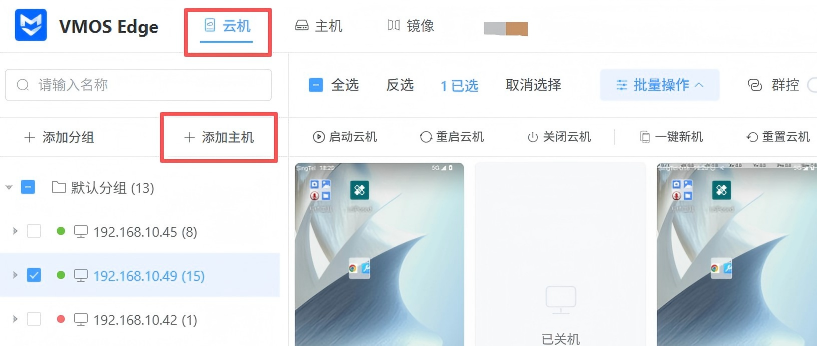
- Manual addition: On the “Cloud Machine” page, click “Add Host” on the left, then enter the LAN IP address of the compute box to bind it.
- Group management: Hosts are stored in the “Default Group” by default. You can create custom groups and move hosts into them for logical classification.
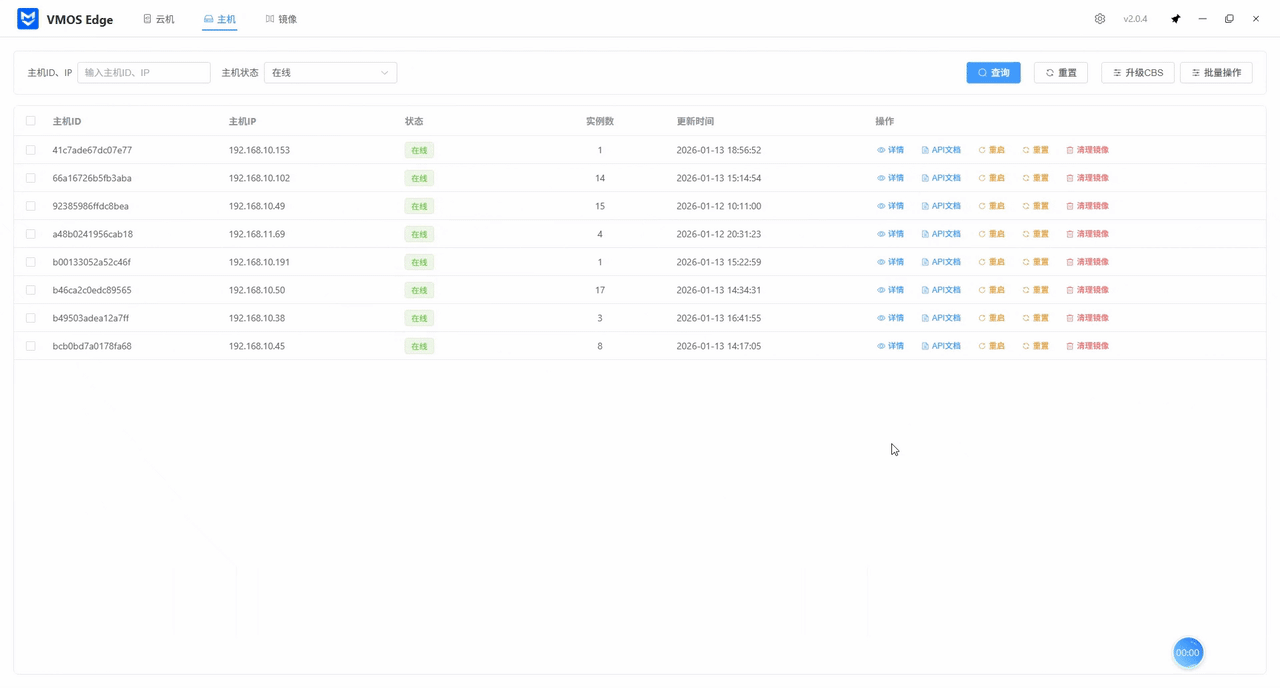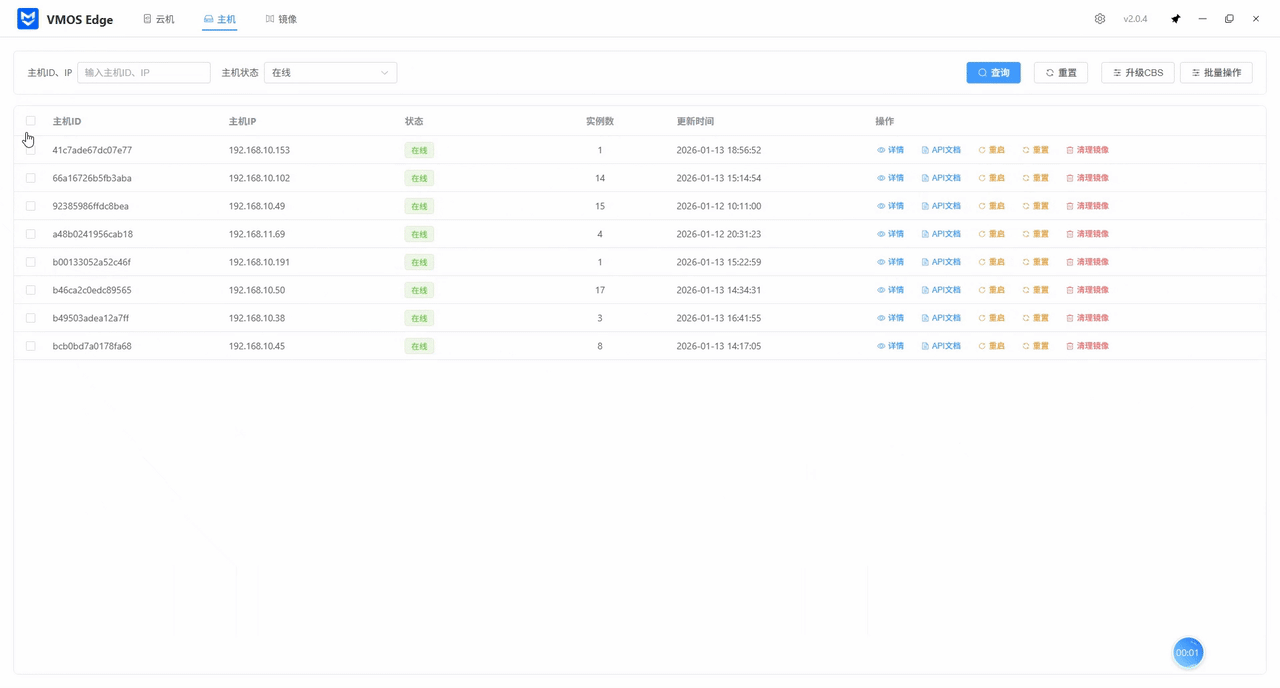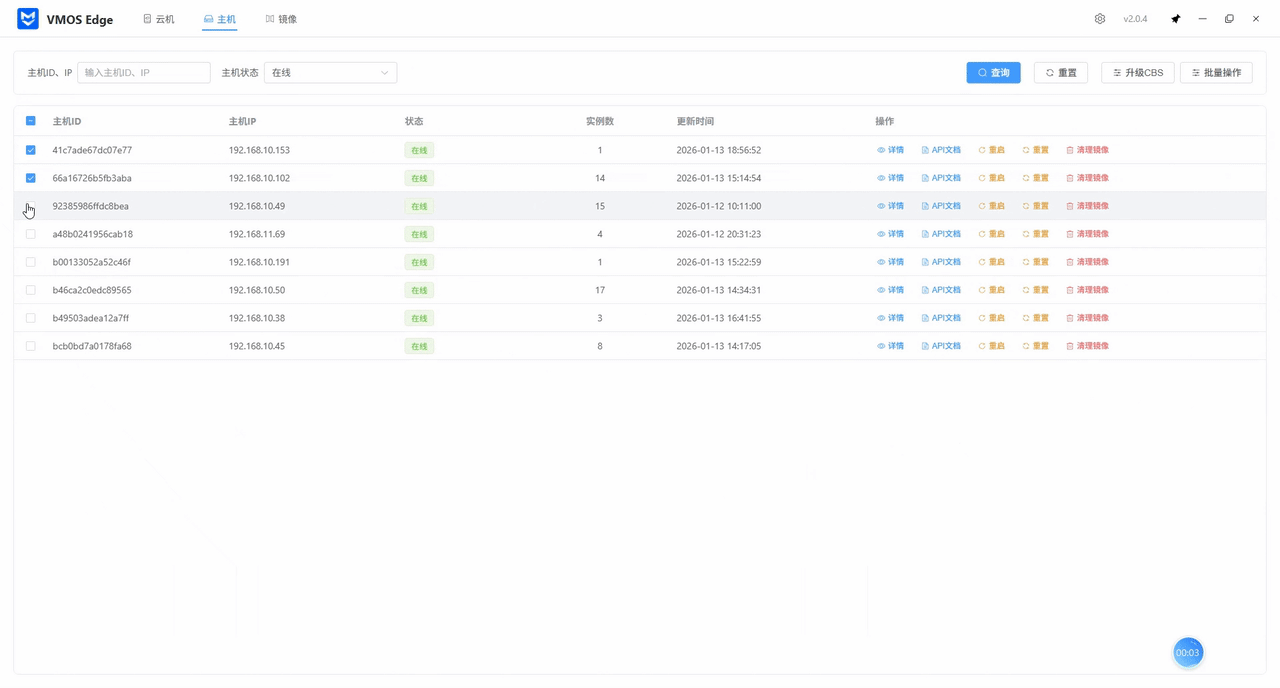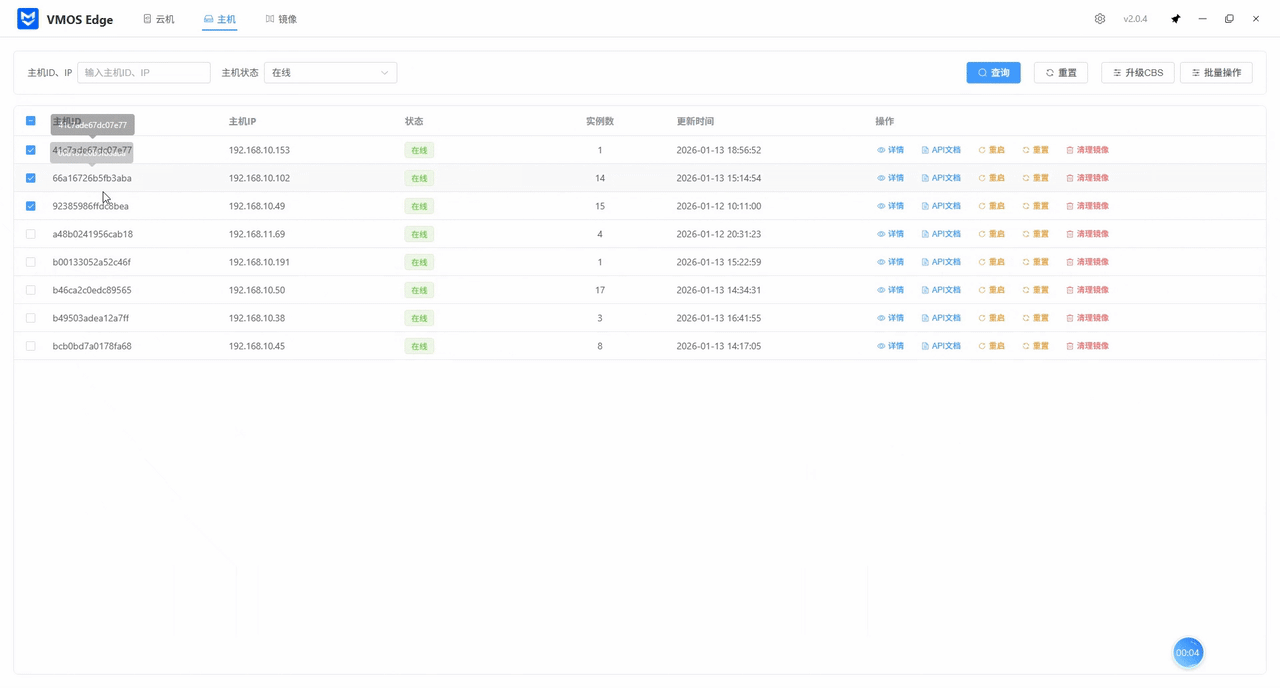
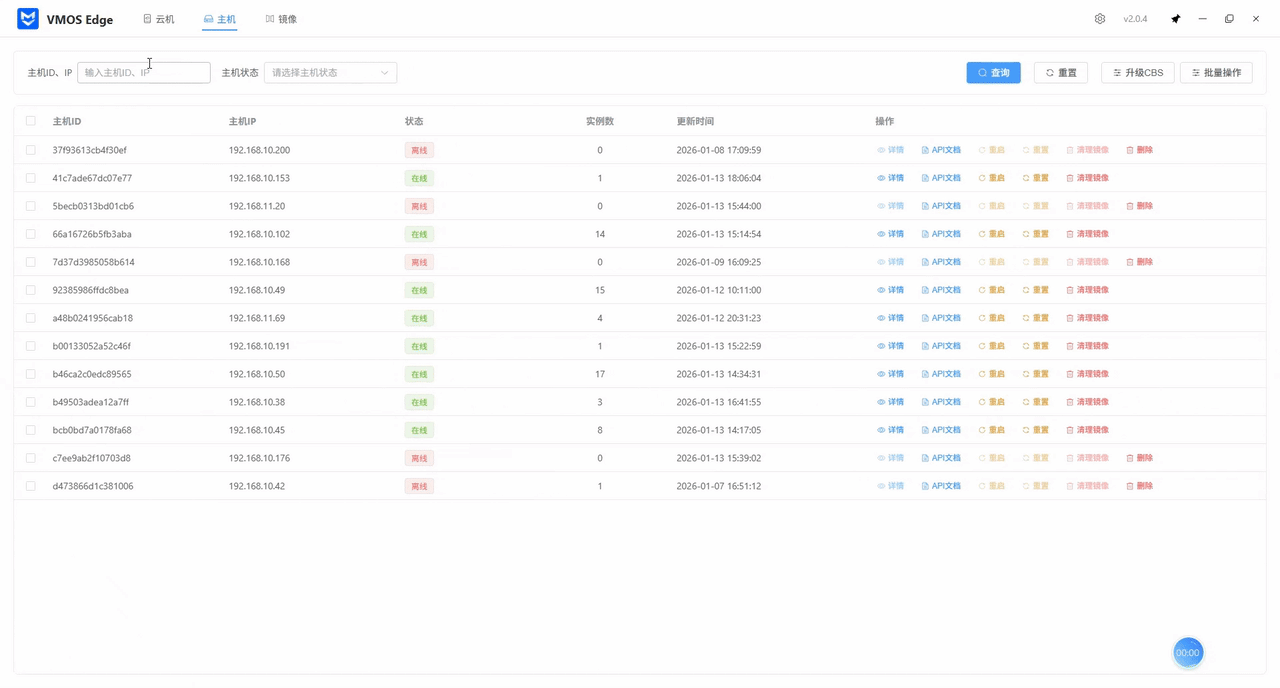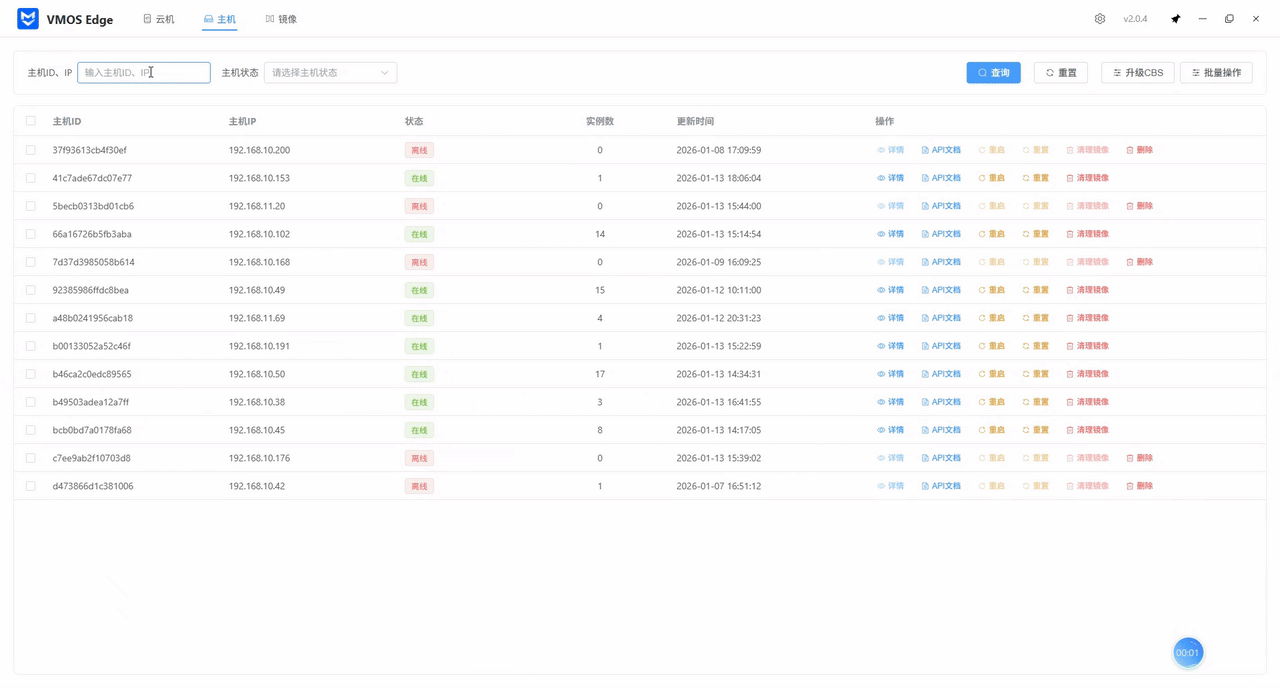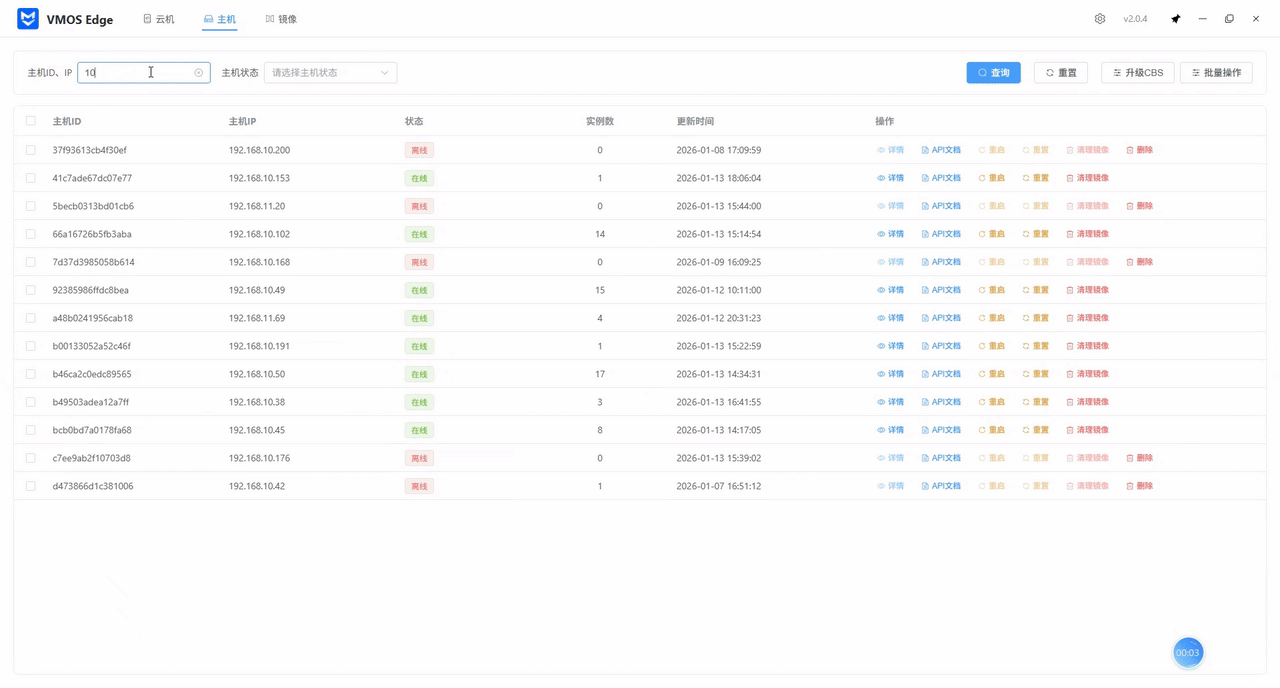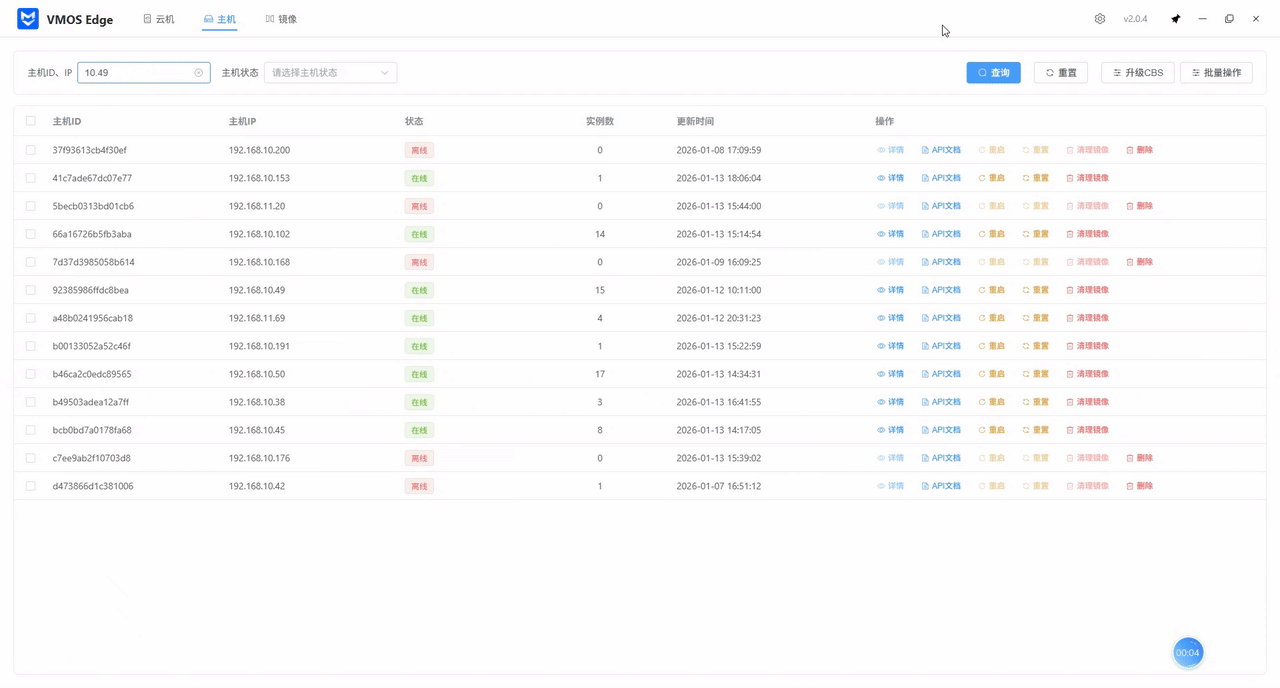
Step 2: Filter and Locate Targets
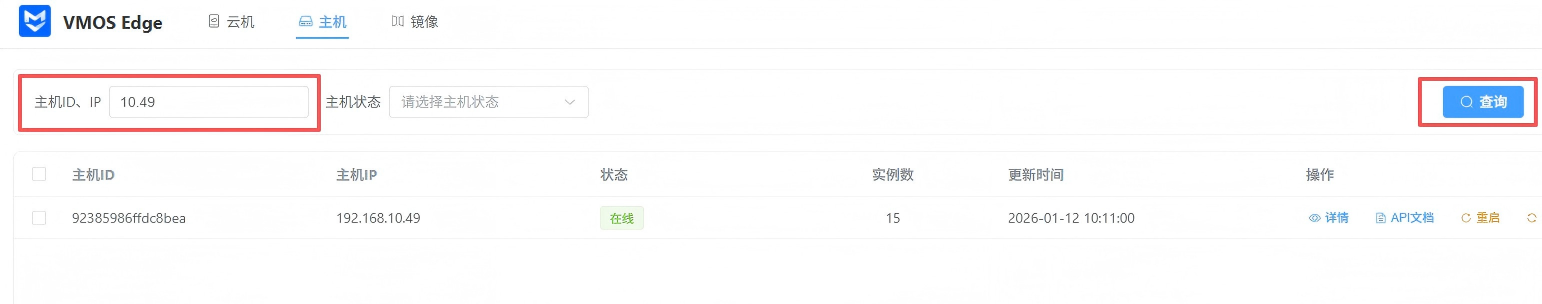
When there are many hosts, use the search area at the top to quickly locate:
- Keyword search: Enter host ID or IP address for precise matching.
- Status filter: Use the “Host Status” dropdown to filter “Online” or “Offline” hosts.
Step 3: Issue O&M Commands
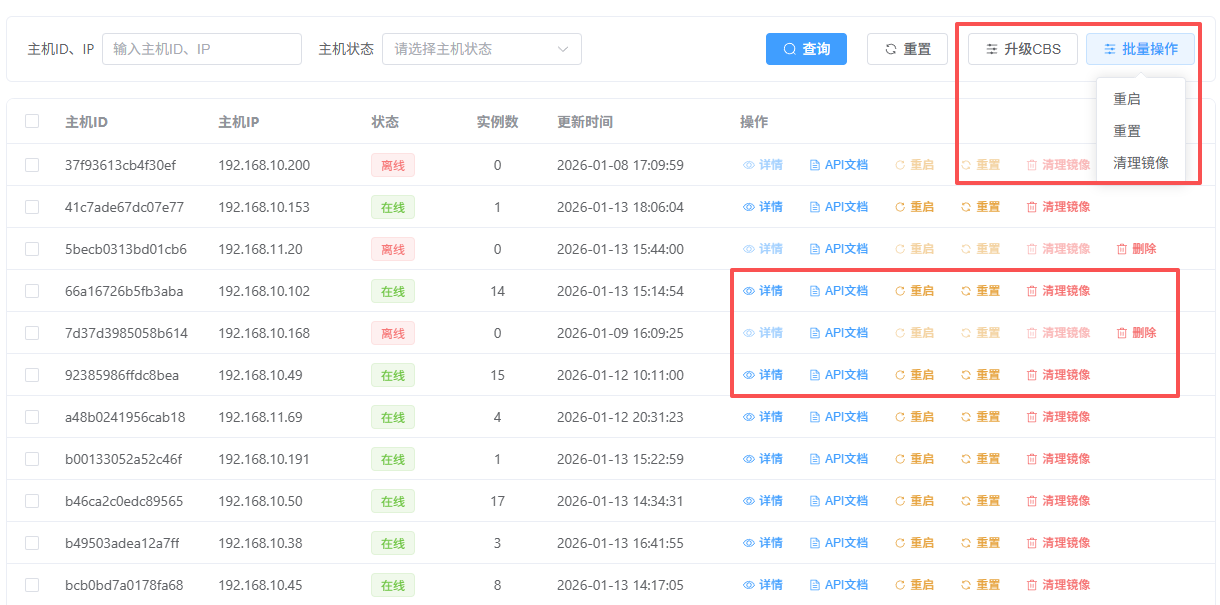
In the operation column, you can execute specific commands on single or multiple hosts:
1. Basic Maintenance
- Restart Host: Remotely restart a VMOS device; this does not affect stored data.
- View Details: Click “Details” to view hardware resource load, network parameters, and an overview of cloud machine instances running on the host.
2. Deep Cleanup and Reset
- Clean Images: Clear unused image packages on the host with one click to free VMOS storage space.
- Reset Host: Use with caution. This clears all cloud machine instances, images, and user data on the host, restoring the device to its initial state.
3. Developer Access and System Upgrades
- API Docs: Quickly jump to the host’s API web page to support developer integration.
- Upgrade CBS: Click the “Upgrade CBS” button at the top to perform a unified version upgrade of the underlying service (cloud machine base) for selected VMOS hosts.
3. Host Details
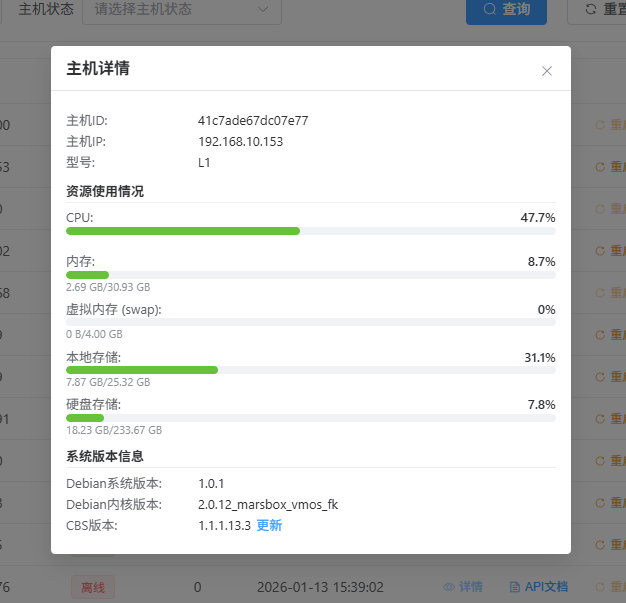
Click the “Details” button in the host list to open the “Host Details” window, which shows the real-time running status and system version information of the physical device.
1. Basic Device Information
- Host ID: The unique management identifier of the device.
- Host IP: The LAN IP address of the device in the current network.
- Model: The specific model of the physical hardware (such as
L1).
2. Resource Utilization (Real-Time Monitoring)
This section shows hardware resource load as percentages and progress bars to help you decide whether to scale out or clean up resources:
- CPU: Current CPU utilization percentage (for example,
14.4%). - Memory: Used memory vs. total memory (for example,
2.07 GB / 30.93 GB) and its proportion. - Virtual Memory (swap): Monitors swap usage to prevent physical memory overflow risks.
- Local Storage: Usage of the system partition on the physical host.
- Disk Storage: Usage of external or built-in large-capacity disks (for example,
18.23 GB / 233.67 GB), typically used to store cloud machine data.
3. System Version Information
Records detailed information about the underlying operating system for technical support and version management:
- Debian OS Version: Version number of the underlying Linux distribution.
- Debian Kernel Version: The currently running Linux kernel information.
- CBS Version: Version number of the backend program that acts as the cloud machine base.
4. Key Business Scenarios SOP
Scenario A: Developer Automation Access
- Use the IP to locate the target device in the host list.
- Confirm that the status is “Online”.
- Click “API Docs” to obtain the interface definitions and keys of the current host for script integration.
Scenario B: Batch System Environment Upgrades
- Select multiple hosts that need to be upgraded.
- Click “Upgrade CBS” in the upper-right corner.
- Upload the new CBS version in the popup dialog; the system will asynchronously execute the upgrade command.